The packaging production process is a fascinating mix of creativity, engineering and precision. Each container we find on the market has gone through a series of crucial stages before reaching our hands. In this blog, we will explore each of these steps, from idea conception to final production, highlighting the importance of each phase in the success of the product. We can indicate that in Selfpackaging the total process usually takes 30 working days, depending on the difficulty of the project-idea.
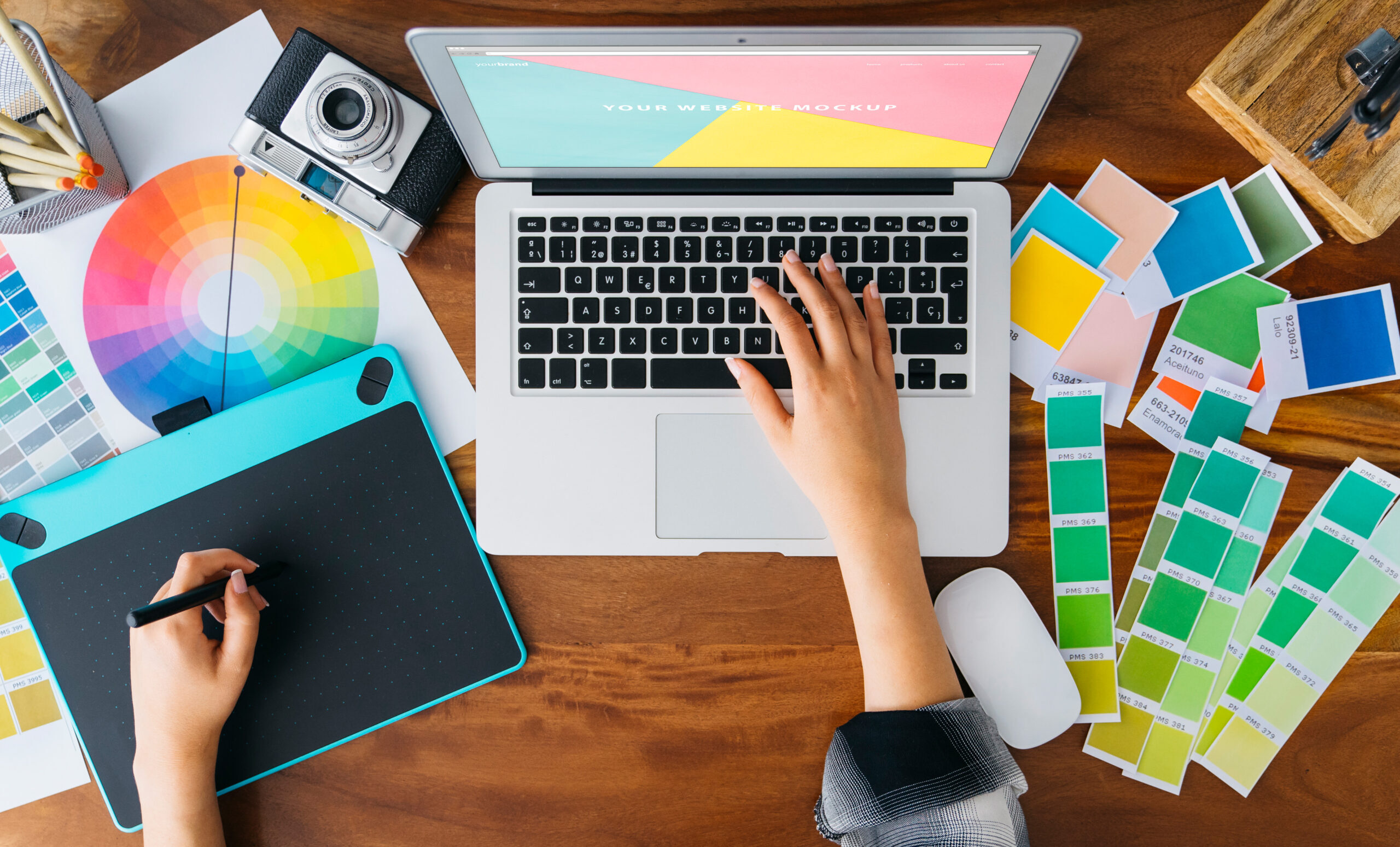

1. Research and Conceptualization
The first step in packaging production is research and conceptualization. This is a collaborative process between designers, marketing and industrial design specialists and the client. Factors such as packaging functionality, user experience, aesthetics and sustainability are considered. During this phase, market studies are carried out to understand current trends and consumer needs. Depending on the complexity of the project, it can last between a few days and several weeks.
Market research is essential to identify consumer preferences and competitors’ strategies. Data is collected on materials, shapes, colors and functions that can influence the purchasing decision. This information helps design teams generate ideas that are innovative and engaging.
2. Design process
Once the idea is defined, the next step is the design. This is where concepts are transformed into visual and structural proposals. Graphic design and CAD (computer-aided design) tools are used to create digital sketches and prototypes. The design must be attractive and functional, ensuring that the product is protected and easy to use.
The design process involves multiple iterations. Designers work closely with engineers and materials specialists to ensure that the packaging is not only aesthetically pleasing, but also practical and efficient in terms of production and use. Aspects such as ergonomics, ease of opening and closing, and presentation at the point of sale are taken into account.
Again, this process can take anywhere from a couple of days to several weeks.

3. Creation and manufacturing of the prototype or model
It is This step is a critical phase in which physical models-prototypes of the packaging are created. These prototypes allow you to evaluate the shape, size, functionality and appearance of the packaging in the real world. Often, several prototypes are produced before arriving at a final version that meets all requirements.
Prototypes are tested in different conditions to ensure that the design is robust and functional. Adjustments can be made to dimensions, material or graphic design based on the results obtained. The goal is to create a prototype that accurately reflects the final product and that can be efficiently produced on a large scale.
This mockup creation process usually takes 2 days to 1 week in our studio.
4. Material selection
Choosing the right materials is essential for packaging success. Aspects such as durability, sustainability, cost and compatibility with the product must be considered. Currently, there is a growing trend towards the use of ecological and recyclable materials, reflecting the growing concern for the environment. We have our FSC certificate that the client can use at any time when printing their packaging.
The selection of materials also involves evaluating their physical and chemical properties. For example, for food products, it is crucial to choose materials that are safe for food contact and that protect against contamination and spoilage. For electronic products, materials that offer protection against impacts and static, etc. should be considered.
5. Tests and adjustments
Before mass production, extensive testing is essential. These tests may include material strength, seal integrity, protection against moisture and other environmental factors. Based on the results of these tests, adjustments are made to optimize the design and materials.
Testing may also include user experience evaluations. Usability studies are carried out to ensure that the packaging is easy to open, close and handle. User feedback can lead to design changes to improve comfort and consumer satisfaction.
In addition, color tests can sometimes be included to try to achieve the desired tone in mass production, since depending on the material to be printed, the colors may vary in tone.
6. Production
Once the design and materials have been approved, mass production begins. This process involves specialized machinery to cut, mold, print and assemble the packaging. Quality and consistency are crucial at this stage, which is why strict quality controls are implemented.
Production can involve several techniques, die-cutting, offset or digital printing, screen printing… Each technique has its own advantages and is selected based on the type of packaging and production volume. Production efficiency is key to keeping costs low and meeting delivery times, which in Selfpackaging are usually 15 business days or 20 business days in the case of more premium boxes such as lined rigid boxes, which require more production work. and elaboration behind.

Besides, the Printing is a vital component of packaging, as it conveys the brand and product information. Printing techniques can vary from screen printing, offset, flexography to digital printing, depending on the needs of the project. In addition, special finishes, such as varnishes, laminates or prints, can be applied to improve the appearance and durability of the packaging.
The choice of colors, fonts and graphics is essential to create attractive packaging that is consistent with the brand identity. Special finishes, such as embossing or foil stamping, can add a touch of luxury and differentiation. The printing must be sharp and durable, resisting wear and maintaining the legibility of the information.
7. Packaging and distribution
Once the packaging is finished, we proceed to packaging the product. This stage includes inserting the product into the container, sealing and labeling. The packaged products are then distributed to points of sale or directly to consumers.
The packaging process must be efficient and ensure that products reach their destination in perfect condition. Automated systems are used to insert, seal and label products quickly and accurately. In addition, logistics and transportation are considered, ensuring that the packaging is resistant and optimized for storage and distribution.
Depending on the destination, the order can arrive between 24 – 48 hours (if it is the peninsula) or 1 week for the rest of Europe.

The packaging production process is complex and multifaceted, requiring the collaboration of various professionals and the integration of multiple technologies. From the initial idea to the final product, each stage is crucial to ensure that the packaging not only protects the product, but also attracts consumers and reflects the brand values. In a world increasingly aware of sustainability, the future of packaging is also evolving towards more ecological and responsible solutions.
Furthermore, innovation in materials and production technologies is opening up new possibilities for packaging, allowing for more creative and functional designs. Companies that invest in good packaging design not only improve the consumer experience, but can also reduce costs and minimize their environmental impact. In short, packaging is much more than a simple box or wrapper; It is an essential part of the marketing strategy and a key tool for the success of any product on the market.

